Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) system offers a sophisticated solution to climate control.
VRF systems ensure optimal comfort by precisely adjusting the temperature in each room. With VRF, you get a seamless, tailored heating and cooling experience that is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
In this guide, Season Control HVAC shares tips on how to optimize HVAC systems with VRF.
Understanding Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Technology
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) technology stands out in climate control. It shifts from the one-size-fits-all approach of traditional HVAC systems by offering precise refrigerant adjustment, matching each zone’s needs in a building.
This leads to more comfort and less energy use.
A VRF system has three parts:
- Outdoor Units: Serve as the power source for the VRF system. They house the compressors and condensers that generate the refrigerant flow.
- Indoor Units: Installed in different zones for precise cooling or heating. They can vary in type, such as wall-mounted, ceiling-suspended, or floor-standing units to suit space requirements.
- Control System: The central intelligence of the VRF system. It monitors and adjusts the refrigerant flow to the indoor units based on each zone’s temperature settings and demands.
The core of VRF operation lies in its ability to vary refrigerant flow. It responds to each zone’s demand, increasing or decreasing flow. This means it can cool one room while heating another, all based on real-time needs.
Advantages of VRF Systems
The VRF systems offer a range of advantages over traditional HVAC solutions, setting a new standard for efficiency, flexibility, and comfort in climate control:
- Energy Efficiency: VRF systems minimize energy waste by precisely matching the cooling or heating output to the demand in each zone. This targeted approach reduces energy consumption and utility costs.
- Flexibility in Design: VRF systems’ modular nature allows for customization to a building’s specific needs. Whether it’s a commercial space, a residential area, or a mixed-use development, VRF can adapt to varied layouts and design requirements.
- Improved Comfort: VRF technology enables individualized temperature control in different zones or rooms. Occupants can enjoy a personalized climate according to their preferred comfort level.
- Quiet Operation: VRF systems have a silent performance and are ideal for environments where noise levels are a concern, such as hospitals, schools, and residential areas.
- Lower Operational Costs: The efficiency and adaptability of VRF systems result in lower operational costs over time. Operating at varying speeds allows them to use only the energy needed. This reduces wear and tear on components and extends the system’s lifespan.
- Simplified Installation and Maintenance: With fewer components and less ductwork than traditional systems, VRF systems are easier and quicker to install. Their design also simplifies maintenance, with advanced diagnostics that help in quick troubleshooting and repair.
Installation Considerations for VRF Systems
Space Requirements
VRF systems are popular for their space-saving features. Traditional HVAC systems require extensive ductwork and large mechanical rooms. However, VRF units are more compact and require less space for installation.
This makes them ideal for buildings with limited space or where preserving architectural integrity is essential.
When considering their installation, plan the proper placement of indoor and outdoor units to ensure optimal performance and accessibility for maintenance.
Cost Analysis
Upfront, VRF systems are more expensive than their traditional counterparts due to their advanced technology and the need for specialized installation.
However, long-term energy costs and maintenance savings can offset this initial investment. The efficiency of VRF systems, particularly in energy use, leads to lower utility bills. Additionally, controlling individual zones reduces wear and tear on the system over time.
Selecting the Right VRF System
Choosing the right VRF system requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Building Size: The size and layout of the building will influence the capacity and configuration of the VRF system needed. Larger buildings may require multiple outdoor units or a combination of types to cover all zones adequately.
- Climate: The climate affects the choice of a VRF system, especially the system’s heating and cooling capacity. Areas with extreme temperatures may require systems with enhanced performance features.
- Specific Needs: Consider the requirements of the occupants and the building. For example, a residential building may prioritize quiet operation, while a commercial building might focus on flexibility and energy efficiency.
How to Maintain Your VRF System?
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of your system and ensures peak performance for optimal comfort.
Here are key tips for maintaining your VRF system:
Regular Inspections
Keep an eye on your system’s efficiency. Any sudden changes in performance could indicate an issue needing attention.
Hire a professional HVAC maintenance service to inspect your VRF system at least once a year. These inspections identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Work with your HVAC professional to develop a long-term maintenance plan tailored to your VRF system. This plan should include regular check-ups, cleaning schedules, and a timeline for potential upgrades or replacements.
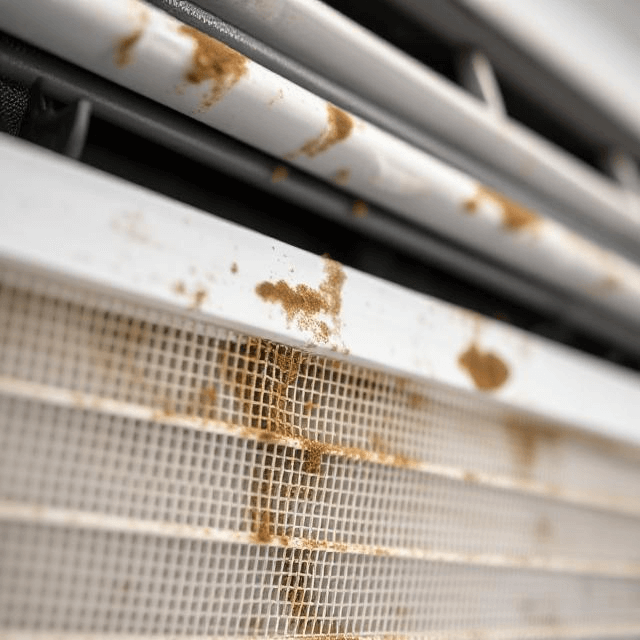
Cleaning Components
- Clean Filters Regularly: You must clean indoor unit filters every few months or more frequently if the environment is dusty. Clean filters improve system performance and indoor air quality.
- Inspect and Clean Outdoor Units: Ensure the outdoor unit is free from debris, leaves, or dirt that can obstruct airflow and reduce efficiency. Check these units periodically, especially after bad weather.
System Updates and Checks
- Software Updates: Like any advanced technology, your VRF system’s control software may require updates. Check with your system’s manufacturer or installer for any updates to ensure optimal performance.
- Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can decrease the efficiency of your VRF system and indicate leaks. Have a technician check refrigerant levels during routine maintenance visits.
Address Repairs Promptly
If an inspection uncovers any issues, address them promptly. Neglecting repairs leads to more significant problems and potentially costly downtime.
Training for Users
- Understand Your System: Familiarize yourself with the basic operation of your VRF system. Knowing how to use the control system properly can prevent unnecessary strain and optimize performance.
- Educate Building Occupants: If applicable, educate others in the building on the proper use of the VRF system to prevent misuse and ensure its efficient operation.
Ready to Optimize Your Indoor Climate?
Optimizing your HVAC with Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) technology elevates comfort and lowers energy costs.
Whether you’re upgrading an existing system or installing a new one, the advantages of VRF technology make it a smart choice for any setting.